To measure the effectiveness of an educational program, evaluate student outcomes and gather feedback from participants. Assess improvements in knowledge, skills, and engagement.
Evaluating the effectiveness of an educational program is crucial for continuous improvement. Effective programs boost student outcomes, enhance skills, and foster engagement. Use quantitative metrics like test scores, graduation rates, and job placements. Qualitative feedback from students, teachers, and employers provides deeper insights.
Regular assessments and surveys identify strengths and areas needing improvement. Align program goals with measurable outcomes to track progress accurately. Implementing these strategies ensures the program remains relevant and impactful. Continuous evaluation helps adapt to changing educational needs, ultimately benefiting students and society.
Importance Of Measuring Effectiveness
Understanding the effectiveness of an educational program is crucial. It helps identify strengths and areas needing improvement. Measuring effectiveness ensures that the program delivers value and achieves its goals.
Why It Matters
Measuring effectiveness helps to determine if students learn effectively. It provides data to improve teaching methods. Effective measurement ensures resources are used wisely. Schools can track progress over time with accurate data.
Impact On Stakeholders
Students benefit directly from effective educational programs. They gain better knowledge and skills. Teachers can refine their teaching strategies based on results. This leads to improved student outcomes.
Parents get assurance that their children receive quality education. They can see the progress and areas of improvement. Administrators can allocate resources more efficiently. They can make informed decisions on curriculum changes.
Policymakers rely on this data for developing educational policies. They can ensure that programs meet educational standards. Effective measurement supports continuous improvement in education.
| Stakeholder | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Students | Gain better knowledge and skills |
| Teachers | Refine teaching strategies |
| Parents | Assurance of quality education |
| Administrators | Efficient resource allocation |
| Policymakers | Development of educational policies |
- Identify strengths and weaknesses
- Ensure resources are used effectively
- Track progress over time
Setting Clear Objectives
Measuring the effectiveness of an educational program starts with setting clear objectives. These objectives act as a roadmap for success. They help educators and administrators stay on track. Let’s explore how to set these objectives effectively.
Defining Goals
Begin by defining specific goals for the educational program. Clear goals make it easier to measure success. Use the SMART criteria:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Ensure you can track progress with data.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals within your resources.
- Relevant: Align goals with the program’s purpose.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving the goals.
For example, a goal might be: “Improve student math scores by 15% in one year.”
Aligning With Standards
Align the program’s objectives with educational standards. Standards ensure consistency and quality in education. Check national or state standards for guidance. This alignment helps to maintain high-quality education.
Create a table to track alignment:
| Objective | Standard |
|---|---|
| Improve math scores | Common Core State Standards |
| Enhance reading skills | State Reading Standards |
Regularly review and update objectives to stay aligned with standards. This practice ensures that the program remains effective and relevant.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative methods are essential in measuring the effectiveness of an educational program. They provide objective data and statistical evidence. These methods help educators make informed decisions. Below are two vital quantitative methods:
Standardized Testing
Standardized testing is a common method for evaluating student performance. These tests are consistent and objective. They measure students’ knowledge and skills in various subjects.
- Benefits:
- Provides a clear benchmark for all students.
- Helps identify areas needing improvement.
- Offers data for comparing different groups.
- Drawbacks:
- May not cover all aspects of learning.
- Can create stress among students.
- Often focuses on memorization over understanding.
Data Analytics
Data analytics uses software tools to interpret vast amounts of educational data. This method helps track student progress and program effectiveness.
- Key Metrics:
- Attendance rates.
- Grades and test scores.
- Graduation rates.
- Benefits:
- Provides real-time insights.
- Identifies trends and patterns.
- Helps personalize learning experiences.
Both standardized testing and data analytics are powerful quantitative methods. They offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of educational programs. Using both methods together can provide a complete picture. This ensures educational programs are meeting their goals.
Qualitative Methods
Measuring the effectiveness of an educational program requires a multi-faceted approach. Qualitative methods provide in-depth insights that quantitative methods often miss. These methods help understand the experiences and perceptions of the participants. They offer a more nuanced view of the program’s impact. Below, we explore two key qualitative methods: Surveys and Questionnaires, and Focus Groups.
Surveys And Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are essential tools in qualitative research. They allow for the collection of detailed feedback from participants. They can capture a wide range of responses.
- Open-ended questions help gather detailed opinions and experiences.
- Closed-ended questions can be used to gather specific data.
Surveys can be distributed online or on paper. They should be easy to understand and complete. Questionnaires should include a mix of question types to gather comprehensive insights.
| Question Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Open-ended | Gather detailed responses |
| Closed-ended | Collect specific data points |
Focus Groups
Focus groups are another valuable method for qualitative research. They involve a small group of participants discussing their experiences. A moderator guides the discussion with prepared questions.
- Select a diverse group of participants to get varied perspectives.
- Prepare a set of questions that address key aspects of the program.
- Record the session for later analysis.
Focus groups provide rich, detailed insights. They help uncover nuances that surveys might miss. The discussions can reveal shared experiences and common challenges.
Both surveys and focus groups are crucial for understanding the full impact of an educational program. They offer insights that numbers alone cannot provide.
Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies are a powerful tool to measure educational programs. These studies track the same participants over a long time. They provide valuable insights into learning and development.
Tracking Progress Over Time
Longitudinal studies excel at tracking progress over time. Schools can monitor students’ achievements from kindergarten to high school. This consistent tracking helps identify trends and patterns.
Teachers can use data to adjust teaching methods. They can see what works best for each student. This continuous assessment helps in personalized learning.
- Monitor student growth
- Identify successful teaching methods
- Adjust curriculum based on findings
Case Studies
Case studies are another form of longitudinal research. They focus on individual or group experiences. These studies provide a detailed look at specific educational programs.
Schools can analyze these case studies to find best practices. They can learn from both successes and failures. This information helps in refining educational strategies.
Here is a simple table to show how case studies can be used:
| Case Study | Findings | Application |
|---|---|---|
| School A | Improved math scores with new curriculum | Adopt similar methods in other schools |
| School B | Increased student engagement with tech tools | Integrate more tech in classrooms |
Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis is a powerful tool. It helps to measure the effectiveness of an educational program. By comparing data, you can see what works best. This method provides clear insights. It highlights the strengths and weaknesses of a program.
Benchmarking Against Others
Benchmarking means comparing your program to others. This shows where your program stands. It helps to identify best practices. You can see which methods are successful. This comparison helps to set realistic goals.
| Criteria | Your Program | Top Program |
|---|---|---|
| Student Performance | 75% | 90% |
| Graduation Rate | 85% | 95% |
| Teacher Satisfaction | 80% | 88% |
Internal Comparisons
Internal comparisons focus on your program alone. Track progress over time. This shows improvement or decline. Compare different parts of the program. See which parts are working well. This method identifies areas that need improvement.
- Compare test scores from different years.
- Analyze student feedback over time.
- Evaluate teacher performance regularly.
Using both benchmarking and internal comparisons provides a full picture. It ensures your program is effective and continuously improving.
Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback mechanisms are vital for measuring the effectiveness of an educational program. They provide direct insights from those involved. This helps in making informed decisions for improvements.
Student Feedback
Student feedback offers a unique perspective. Students are the primary beneficiaries of the program. Their opinions matter the most. Collecting student feedback can be done in several ways:
- Surveys: Quick and easy to fill out.
- Focus groups: In-depth discussions with selected students.
- Suggestion boxes: Anonymous and honest feedback.
Using these methods, you can gather valuable insights. This helps in understanding what works and what needs change.
Teacher Evaluations
Teacher evaluations are equally important. Teachers interact with students daily. They can provide detailed feedback on the program’s effectiveness. Some ways to gather teacher evaluations include:
- Regular meetings: Discuss progress and challenges.
- Written reports: Detailed analysis of the educational program.
- Peer reviews: Teachers reviewing each other’s methods.
These evaluations help in identifying strengths and weaknesses. This ensures continuous improvement of the educational program.
Credit: education.musc.edu
Interpreting Results
Interpreting the results of an educational program is crucial. This step helps understand the program’s impact on students. Effective interpretation involves analyzing data and reporting findings clearly. Below are key areas to focus on:
Analyzing Data
Analyzing data involves breaking down information into understandable parts. Use statistical tools to identify trends and patterns. Here are some steps:
- Collect Data: Gather data through surveys, tests, and observations.
- Clean Data: Remove any errors or inconsistencies in the data.
- Organize Data: Use tables or charts to arrange data logically.
For example:
| Metric | Before Program | After Program |
|---|---|---|
| Test Scores | 70% | 85% |
| Attendance | 80% | 95% |
Reporting Findings
Report findings in a clear and concise manner. Use visuals to make data more understandable. Follow these steps:
- Create Charts: Use bar or pie charts to represent data visually.
- Write Summary: Summarize key findings in simple language.
- Highlight Success: Point out significant improvements and achievements.
For instance:
- Test scores improved by 15% after the program. This shows a clear benefit.
- Visual aids help readers grasp complex information quickly. They make reports more engaging.
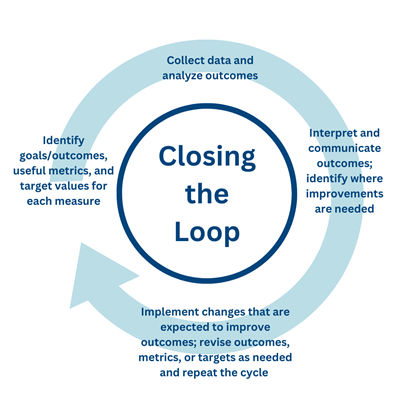
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a critical component in measuring the effectiveness of an educational program. By constantly assessing and refining teaching methods, schools can ensure the best learning outcomes for students. This process involves implementing changes and monitoring ongoing performance to identify areas for enhancement.
Implementing Changes
Once you collect data and feedback, it’s essential to implement changes. Use both qualitative and quantitative data to guide your decisions. Focus on areas that need immediate improvement.
Here are steps to follow:
- Identify specific gaps in student learning.
- Develop a plan to address these gaps.
- Train educators on new methods and tools.
- Allocate resources efficiently to support changes.
For example, if students struggle with reading comprehension, introduce new reading materials and techniques. Regularly update curriculum materials to keep them relevant and engaging.
Monitoring Ongoing Performance
After implementing changes, ongoing performance monitoring is crucial. Regularly check if the new methods are effective.
Use the following tools to monitor performance:
- Surveys: Gather student, parent, and teacher feedback.
- Standardized Tests: Measure academic progress objectively.
- Classroom Observations: Assess teaching practices and student engagement.
- Data Analytics: Track attendance, grades, and participation rates.
Create a monitoring schedule to ensure consistency. Track improvements and identify areas needing further adjustment. This ensures that your educational program remains dynamic and effective.
Below is a sample table to track ongoing performance:
| Metric | Frequency | Responsible Person | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survey Feedback | Monthly | Program Coordinator | Analyze for trends |
| Standardized Tests | Quarterly | Testing Coordinator | Compare year-over-year |
| Classroom Observations | Bi-Weekly | Principal | Note teaching practices |
| Data Analytics | Weekly | Data Analyst | Track key metrics |

Credit: www.linkedin.com
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Frequently Asked Questions
How To Assess The Effectiveness Of An Educational Program?
Evaluate the effectiveness of an educational program by measuring student progress, engagement, and feedback. Analyze test scores, completion rates, and surveys to gain insights.
How Do You Measure Effectiveness In Education?
Effectiveness in education is measured by student performance, engagement levels, graduation rates, and standardized test scores. Teacher evaluations and feedback also play a crucial role.
How To Measure The Success Of An Education Program?
Measure the success of an education program by tracking student performance, graduation rates, job placements, and feedback. Assess engagement through attendance and participation. Use standardized tests, surveys, and data analytics for accurate insights.
How Would You Evaluate The Effectiveness Of An Educational Training Program?
Evaluate effectiveness by assessing participant feedback, test scores, skill application, and training completion rates. Measure improvements in performance and knowledge retention. Use surveys and assessments.
Conclusion
Evaluating educational programs is crucial for continuous improvement. Use metrics like student performance, engagement, and feedback to gauge success. Regular assessments help identify strengths and areas for enhancement. Implement these strategies to ensure your educational program delivers the desired outcomes.
Consistent evaluation leads to better learning experiences and improved educational effectiveness.