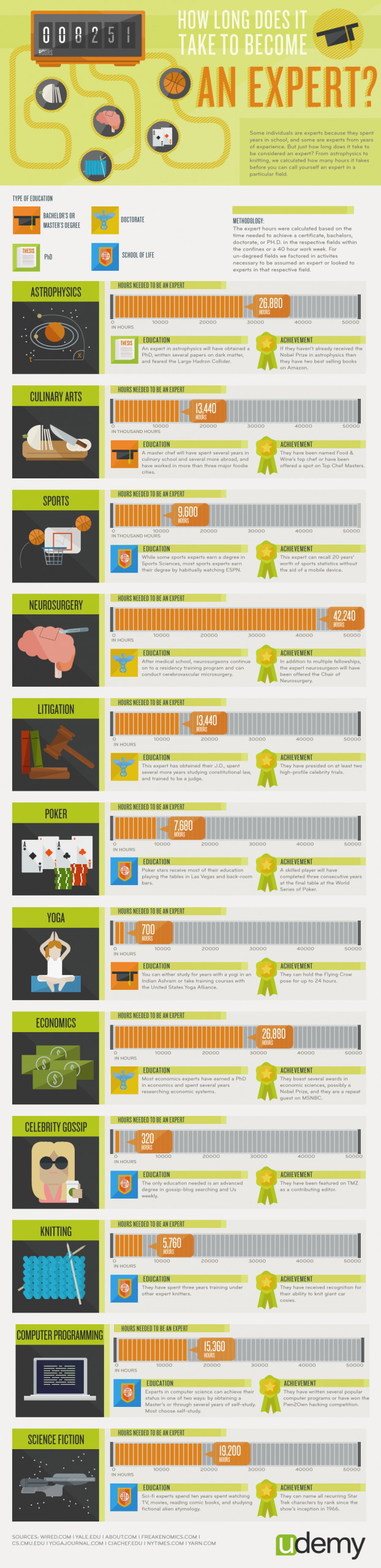
It typically takes around 10,000 hours of deliberate practice to become an expert in a field. This equates to roughly 10 years.
Becoming an expert is a journey that demands dedication, consistent effort, and a structured approach. Experts often combine formal education, hands-on experience, and continuous learning. Engaging in deliberate practice, seeking mentorship, and staying updated with industry trends are crucial. Regularly setting and achieving small goals helps maintain motivation.
It’s essential to develop problem-solving skills and a deep understanding of the subject. Networking with other professionals can provide valuable insights and opportunities. Remember, persistence and passion play significant roles in this long-term commitment. The path to expertise is challenging but rewarding, offering personal and professional growth.
The Concept Of Expertise
Becoming an expert is a journey filled with learning and practice. It involves dedication, patience, and continuous effort. Understanding the concept of expertise helps in setting realistic expectations and goals. Let’s dive deeper into what it means to be an expert.
Defining Expertise
Expertise refers to a high level of skill or knowledge in a particular field. An expert is someone recognized for their deep understanding and ability to perform at a high level.
- Knowledge: Comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
- Skills: Ability to apply knowledge effectively.
- Experience: Practical exposure and hands-on practice over time.
Experts often spend years honing their skills. They learn from both successes and failures. Their insights are valuable and trusted by others.
Levels Of Skill
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Beginner | Basic understanding and starting to learn the fundamentals. |
| Intermediate | Better grasp of concepts and able to perform tasks with some guidance. |
| Advanced | Strong knowledge and capable of handling complex tasks independently. |
| Expert | Deep understanding and mastery, often recognized by peers. |
Understanding these levels helps in mapping out the journey to expertise. It allows individuals to set achievable goals and measure progress effectively.
Credit: blog.udemy.com
Factors Influencing Expertise
Becoming an expert in any field is a journey influenced by various factors. Understanding these factors can help you plan your path to expertise. Let’s dive into the key elements that play a role in mastering a skill.
Natural Talent
Natural talent refers to the innate abilities one is born with. Some individuals grasp concepts quicker due to their inherent skills. This head start can reduce the time needed to become an expert.
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Faster learning curve | Over-reliance on talent |
| Higher initial performance | Less emphasis on practice |
Practice And Effort
Practice and effort are crucial for achieving expertise. Dedicated practice helps in honing skills and overcoming weaknesses.
- Deliberate Practice: Focus on specific skills needing improvement.
- Consistency: Regular practice sessions enhance skill retention.
- Feedback: Constructive feedback helps in refining techniques.
Consistent effort leads to gradual improvement. This approach ensures a solid foundation and long-term mastery.
The 10,000-hour Rule
The 10,000-Hour Rule suggests that mastering a skill needs 10,000 hours of practice. This idea gained fame through Malcolm Gladwell’s book, “Outliers”. The rule has sparked much debate. Let’s explore its origins and the criticism it faces.
Origins Of The Rule
The 10,000-Hour Rule comes from a study by Anders Ericsson. He researched violinists and noticed top performers practiced more. The concept was then popularized by Malcolm Gladwell. He argued that 10,000 hours of practice leads to mastery.
Ericsson found that practice time was a key factor. It separated good performers from the best. Gladwell took this idea and applied it to various fields. He showed that many experts had invested around 10,000 hours in their craft.
Criticism And Debate
Despite its popularity, the 10,000-Hour Rule has faced criticism. Some argue that quality of practice matters more than quantity. Not all practice is equal. Deliberate practice, focused on improvement, is crucial.
Others point out that innate talent plays a role. Some people learn faster than others. This means they might need fewer hours to become experts. Additionally, passion and motivation are important. They drive consistent practice over time.
Another critique is that the rule oversimplifies mastery. Different skills may require different amounts of practice. For example, becoming a top chess player might need more practice than mastering basic cooking skills.
| Criticism | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Quality vs. Quantity | Focus on deliberate practice, not just hours. |
| Innate Talent | Some learn faster, needing fewer hours. |
| Passion and Motivation | Drive consistent practice. |
| Different Skills | Require varying amounts of practice. |
Deliberate Practice
Deliberate practice is a structured and focused way to improve skills. It involves setting specific goals, receiving feedback, and making adjustments. This method is essential for becoming an expert in any field.
Purposeful Practice
Purposeful practice is not just about repetition. It requires clear objectives and a plan to achieve them. This type of practice helps in developing skills faster.
- Set specific and attainable goals.
- Create a practice schedule.
- Focus on one skill at a time.
Feedback And Improvement
Feedback is crucial for improvement. It helps identify strengths and weaknesses. Regular feedback ensures you stay on the right track.
| Type of Feedback | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Self-assessment | Identify personal progress. |
| Peer reviews | Gain different perspectives. |
| Expert advice | Receive professional guidance. |
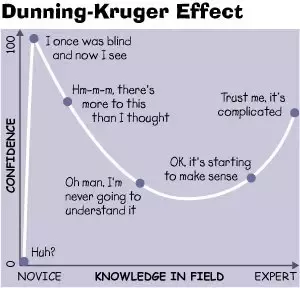
Learning Curves
Understanding learning curves is crucial for becoming an expert. Each person’s journey has unique phases and challenges. Below, we’ll explore these phases in detail.
Initial Learning Phase
In the initial learning phase, everything is new and exciting. You absorb information quickly. Small wins boost your confidence. This phase is often fast-paced.
During this phase, you build a strong foundation. You learn basic skills and concepts. This stage is crucial for long-term success.
Here are some key activities:
- Reading introductory books
- Attending beginner courses
- Practicing basic skills
Plateaus And Breakthroughs
After the initial phase, you may hit a plateau. Progress slows down. This is normal and part of the process. Plateaus can be frustrating but they are temporary.
Breakthroughs often follow plateaus. These moments of insight push you to the next level. Breakthroughs can be triggered by:
- Solving a complex problem
- Gaining new perspectives
- Getting feedback from experts
Recognizing and embracing plateaus and breakthroughs is key. Both are essential to becoming an expert.
| Phase | Description | Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Learning Phase | Fast-paced, foundational learning | Reading, courses, practice |
| Plateaus | Slow progress, frustration | Continued practice, seeking feedback |
| Breakthroughs | Moments of insight, skill improvement | Problem-solving, new perspectives |
Credit: www.quora.com
Role Of Mentorship
Mentorship plays a crucial role in becoming an expert. A mentor offers guidance, support, and valuable insights. Their experience helps you avoid common pitfalls. They can speed up your learning process significantly.
Finding A Mentor
Finding the right mentor is key. Look for someone experienced in your field. They should have a proven track record. They should also be willing to share their knowledge.
You can find mentors in various places:
- Professional networks
- Online communities
- Industry events
- Educational institutions
Approach potential mentors respectfully. Explain why you value their expertise. Be clear about what you hope to learn.
Benefits Of Guidance
Mentorship offers numerous benefits. Here are some key advantages:
- Accelerated Learning: Mentors help you learn faster. They share their experiences and shortcuts.
- Personalized Feedback: A mentor gives tailored advice. This feedback is specific to your needs.
- Networking Opportunities: Mentors often introduce you to key contacts. This expands your professional network.
- Confidence Boost: Regular support from a mentor boosts your confidence. You feel more prepared to face challenges.
Mentors guide you through complex situations. They help you make informed decisions. Their insights save you time and effort.
Tools And Resources
Becoming an expert requires various tools and resources. These help in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge effectively. From educational materials to technological aids, each element plays a critical role in your journey towards expertise.
Educational Materials
Educational materials form the backbone of any learning process. They include books, online courses, and journals. Here are some common types:
- Books: Foundational texts provide deep insights.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and Udemy offer structured learning paths.
- Journals: Research papers keep you updated with the latest developments.
These resources are essential for building a strong knowledge base. They offer both theoretical and practical insights.
Technological Aids
Technological aids make the learning process more efficient and engaging. They include software, apps, and other digital tools. Here are some examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Mind Mapping Software | Organizes thoughts and ideas visually. |
| Learning Management Systems (LMS) | Offers structured courses and tracks progress. |
| Productivity Apps | Helps manage time and tasks efficiently. |
Real-world Examples
Becoming an expert takes time and effort. Real-world examples give us a clear picture. Let’s dive into some inspiring stories and case studies that illustrate this journey.
Case Studies
Case studies show us the detailed paths taken by experts. These real-life examples highlight key milestones and strategies.
| Expert Name | Field | Time to Expertise | Key Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malcolm Gladwell | Writing | 10 Years |
|
| Serena Williams | Tennis | 15 Years |
|
Success Stories
Success stories inspire us with their unique journeys. They show us what is possible.
Bill Gates: Bill Gates started programming at a young age. He spent countless hours coding. He founded Microsoft at 20. After years of hard work, he became a tech mogul.
J.K. Rowling: J.K. Rowling faced many rejections. She spent years writing and refining her craft. Her persistence paid off with the success of Harry Potter.
Elon Musk: Elon Musk’s journey is full of challenges. He started with Zip2, then PayPal, and now leads SpaceX and Tesla. His dedication and vision have made him a leading innovator.
- Identify your passion.
- Dedicate time daily.
- Seek feedback.
- Stay persistent.
- Celebrate small wins.
These examples show that becoming an expert requires dedication and hard work. The journey may vary, but the core principles remain the same.
Balancing Patience And Persistence
Becoming an expert requires both patience and persistence. It’s a journey filled with learning and practice. To stay on track, one must maintain motivation and avoid burnout.
Maintaining Motivation
Motivation is key to becoming an expert. Set small, achievable goals to stay motivated. Celebrate every milestone, no matter how small. This keeps the journey enjoyable.
Form a support network. Surround yourself with like-minded individuals. They can provide encouragement and share useful tips. Also, track your progress. Use a journal or app. Seeing improvement boosts confidence and motivation.
Avoiding Burnout
Burnout can halt your journey to expertise. To avoid it, take regular breaks. Overworking can lead to exhaustion. Breaks help refresh your mind and body.
Create a balanced schedule. Include time for hobbies and relaxation. This ensures you don’t feel overwhelmed. Practice self-care. Eat well, exercise, and get enough sleep. A healthy body supports a healthy mind.
| Tip | Action |
|---|---|
| Set Small Goals | Break down tasks into manageable parts. |
| Track Progress | Use journals or apps to monitor improvement. |
| Take Breaks | Include regular breaks in your schedule. |
| Self-Care | Maintain a healthy lifestyle. |

Credit: www.benchfly.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Until You Are Considered An Expert?
Becoming an expert typically takes around 10,000 hours of practice, roughly equivalent to 5-10 years. Consistent effort and learning are key.
How Many Years Makes Someone An Expert?
Typically, it takes around 10 years of focused practice to become an expert in a field.
What Qualifies Someone As An Expert?
An expert has extensive knowledge, skills, and experience in a specific field. They often hold relevant qualifications and have a proven track record.
How Do You Become An Expert?
Gain expertise through continuous learning, practice, and hands-on experience. Seek mentorship, set goals, and stay updated in your field.
Conclusion
Becoming an expert varies by field and dedication. Consistent practice and learning are essential. Set realistic goals and stay committed. Remember, expertise requires time and patience. Stay motivated and enjoy the journey. With persistence, you will achieve mastery. Keep pushing forward, and success will follow.










